Nucleotides: effect, function & structure
Structure of a nucleotide
Find out how a nucleotide is structured and why they are so important as the basic building blocks of DNA.
Learn moreWhat are the functions of nucleotides?
Would you like to know what function these building blocks fulfill in our body? Find out here how they influence cell division, energy transport and protein biosynthesis.
Learn moreWhat effect do nucleotides have?
Find out what other effects nucleotides trigger in us and what benefits this has for our body.
Learn moreThe importance of vitamins, minerals, trace elements and proteins for our body and our health is widely known today. However, in addition to these nutrients, there are also some that are less well known: nucleotides.
Nucleotides are important building blocks of life and play a crucial role in many processes. They are the building blocks of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA and can act as energy sources, building blocks and signaling molecules and are therefore of crucial importance for the formation of new cells and energy metabolism.
In this article, we will take a closer look at the structure, functions and effects of nucleotides in the body.
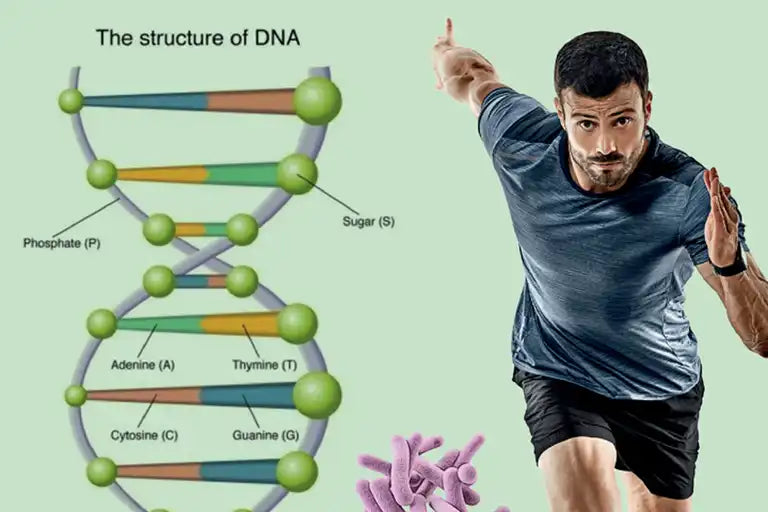
Structure of a nucleotide
Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA and consist of a sugar, an organic base and a phosphate residue. The sugar is either deoxyribose in DNA or ribose in RNA. The organic base can be one of four bases: Adenine, Thymine (only in DNA), Guanine, Cytosine or Uracil (only in RNA). The phosphate residue consists of a phosphate group and is responsible for linking the nucleotides to form a chain.
The nucleotides are connected to each other via so-called phosphodiester bonds, resulting in a single-stranded nucleic acid. In DNA, nucleotides form a double helix by pairing the bases adenine (A) with thymine (T) and guanine (G) with cytosine (C). The fantastic ability of nucleotides to bind together and form a long chain is one of their best features. The structure of a nucleotide is of great importance for its function and effect in the cell. The combination of nucleobase, sugar and phosphate group enables nucleotides to store genetic information, transfer energy and regulate various biochemical processes.
What are the functions of nucleotides?
Nucleotides are involved in numerous metabolic reactions and are therefore considered to be one of the most diverse substances in the human body. Among other things, they are relevant for cell division, energy transport and protein biosynthesis.
- Cell division: Of all the processes that are controlled by nucleotides, cell division is probably the best known. Before cell division can take place, the entire DNA must first double. Around 3 billion nucleotides are required for each cell division. A lack of nucleotides can lead to insufficient DNA replication and impaired cell division, which weakens the immune system and can lead to various diseases and genetic disorders.
- Protein synthesis: Similar to DNA and RNA, nucleotides also serve as important molecules in protein synthesis. The genetic code of DNA determines the arrangement of amino acids in a protein. During the production of proteins, DNA is converted into a messenger RNA molecule (mRNA). The mRNA in turn transmits the genetic code to the ribosomes, which can be described as the cell's protein factories. Based on the instructions of the mRNA, another molecule called tRNA (transfer RNA) then brings the correct amino acids to the ribosomes. The amino acids are finally assembled into a protein by the ribosomes. In this way, nucleotides help to pass on the instructions of the genetic code and ensure that the correct amino acids are used to form proteins during protein synthesis. Consequently, nucleotides are essential for the production of proteins and the associated cell growth. Without them, cells would not be able to produce digestive enzymes, some hormones, hemoglobin for oxygen transport, etc., or only very slowly. This would have an extremely negative effect on our body.
- Energy transport: Another important aspect of nucleotides is their role in energy transport. A nucleotide called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the main energy-rich nucleotide produced in the mitochondria. Mitochondria are the power plants of the cell and produce ATP through the oxidative breakdown of glucose and other energy-rich molecules. ATP then functions as a universal energy carrier. By splitting off a phosphate group from ATP, energy is released that is used by the cells to carry out vital processes such as muscle contractions or the maintenance of cell metabolism. Overall, nucleotides, especially ATP, fulfill an essential function in energy transport within the cells and thus enable the smooth functioning of the organism.
- Immune system & signaling: Nucleotides play a crucial role in the immune system and in the transmission of signals between cells. They are important for the formation of antibodies, which in turn are essential for the defense against pathogens. In addition, nucleotides are also involved in signal transmission between cells and promote the repair and regeneration of damaged tissue and support the growth of new cells. Nucleotides also influence the activity of immune cells and modulate the immune response to pathogens. If the need for nucleotides is not sufficiently met, various bodily functions can no longer function optimally.
Selected products with added nucleotides
What effect do nucleotides have?
Nucleotides have a variety of effects in the body. One of the most important is the formation and repair of DNA and RNA. Without a sufficient supply of nucleotides, the body cannot keep its genetic information intact and may show symptoms such as impaired cell division or a weakened metabolism. Other effects caused by nucleotides are as follows:
- Reduces the possibility of diarrhea.
- They can act as neurotransmitters and have a calming effect on the nervous system.
- Improves the immune system of the human body.
- Nucleotides are useful in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- When stress levels rise, nucleotides help to reduce cortisol levels in humans, a hormone that the body releases in stressful situations.
- The most important element of metabolism is nucleotides, which are essential for the functioning of the liver.
- It helps to increase the number of natural killer cells in the body to prevent the attack of diseases or viruses.
- Improves the efficiency of cell repair and the rapid growth of cells.
- The nutritional nucleotides help fight eczema, repair/fix skin tissue and other skin problems a person may have.
More matching blog articles on the topic of nucleotides
Nucleotides are the building blocks of life and fulfill a variety of important functions in the human body. They are components of DNA and RNA, control cell division, serve as energy carriers and support the immune system. They are also essential for the production of proteins and the associated cell growth. In addition, they can have a calming effect on the nervous system, help with diarrhea, lower cortisol levels and even fight eczema A balanced intake of nucleotides is therefore crucial for a healthy life.







