Scientific background & significance
What are the best nucleotides?
Nucleotides are the fundamental building blocks of DNA and RNA—and therefore essential for all forms of life. They control key processes such as cell division, regeneration, metabolism, and immune defense. While they are produced naturally in the body, demand increases particularly during times of increased stress, illness, and performance-oriented sports.
Nucleotides are essential for cell division, cell renewal and immune defense.
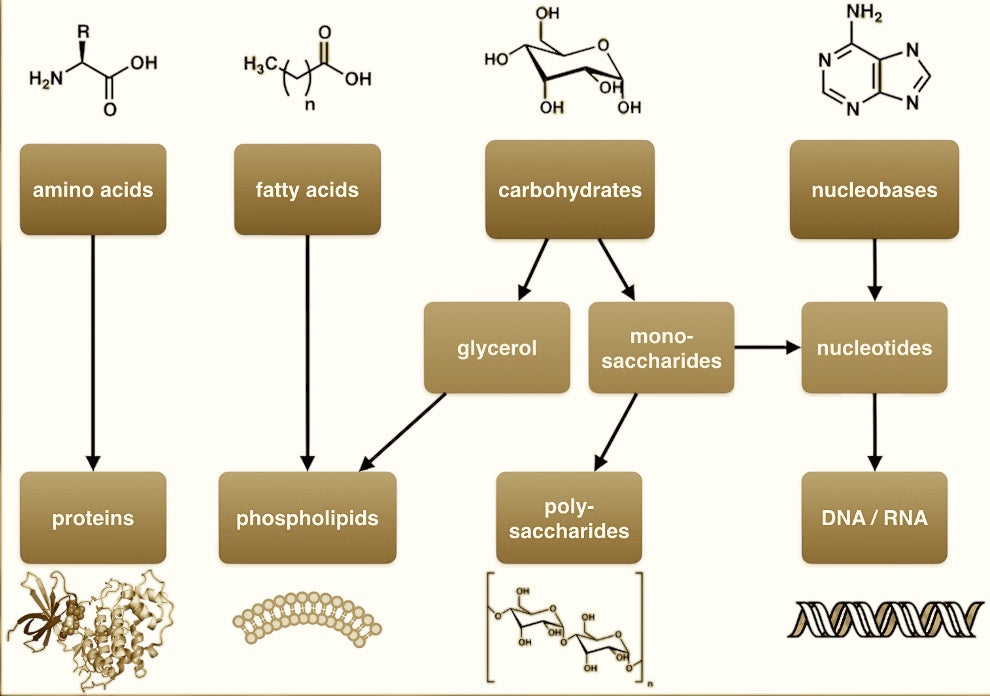
Nucleotides consist of three basic building blocks: a sugar component, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. These seemingly simple molecules are involved in virtually all key biological processes:
- Cell division & growth: Nucleotides enable the replication of genetic information and thus the formation of new cells—essential for growth, regeneration after injury, and the maintenance of healthy tissue.
- Immune function: The immune system needs nucleotides for the rapid proliferation of immune cells and effective defense against pathogens. During periods of stress or strain, the body's demand for nucleotides can increase significantly.
- Energy and metabolism: ATP, the universal "energy molecule" in every cell of the body, is itself a nucleotide. Other metabolic processes (e.g., signal transmission, detoxification) also depend on nucleotides.
- Gut health: Cells with a high division rate—such as those in the intestinal mucosa—benefit particularly from an adequate supply of nucleotides, which can have a positive effect on digestion, nutrient absorption, and general well-being.

Nucleotides in modern nutrition & supplementation
While the body can basically produce nucleotides itself (de novo synthesis), scientific studies show that an additional supply—for example, in the form of dietary supplements—can be useful in certain situations. These include:
- Intense athletic exertion
- Periods of increased regeneration (e.g., after illness, injury, surgery)
- Stress, an unbalanced diet, or limited endogenous synthesis (e.g., in old age)
Vegana Natura relies on individually selected, high-purity nucleotides that are produced in accordance with Swiss quality standards. The formulations are chosen to offer particularly high bioavailability and tolerability—vegan, low in allergens, and free from unwanted additives.
Conclusion
Nucleotides are much more than just DNA building blocks: they are essential for health, performance, and well-being. Targeted supplementation can make a valuable contribution to supporting regeneration, the immune system, and vitality, especially when there is an increased need—scientifically proven and Swiss-made.
Single-selected nucleotides vs. conventional nucleotide sources


Nucleotides are important building blocks of life.
They are still abundant in human breast milk, but later
we often have too few of them in our food. The special structure of nucleotides makes it possible to store and pass on genetic information that every cell needs for its metabolism.
Nucleotides are essential for cell division, cell renewal and immune defense.

What are the functions of nucleotides?
Alongside amino acids and lipids, nucleotides are the most important building blocks of life and therefore also of the human body.
are nucleotides:
- Components of DNA. Genetic information Deoxyribonucleic acid consists of nucleotides. Each time a cell divides, the double strand is halved and joined together with fresh nucleotides. This process alone requires 3 billion nucleotides per cell division.
- essential for the production of proteins. Protein synthesis requires a lot of ribonucleic acid: mRNA is read from DNA and translated into a sequence of amino acids at the ribosomes formed from mRNA. tRNA transports the protein building blocks there and helps with their incorporation.
- serve as a source of energy in our body. Nucleotides provide the energy for numerous metabolic processes. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is our universal energy currency. Cofactors such as coenzyme A (CoA) or nicotinamide dinucleotide (NAD+) are involved in energy transfer.
- helpful messenger substances. Like cyclic AMP (cAMP), nucleotides are indispensable in many signaling pathways.
In principle, the human body can produce nucleotides itself, provided it has the necessary building blocks available. They are therefore not considered essential nutrients, like vitamins or trace elements. However, new synthesis is very complex. Each of them requires at least one phosphate residue, the incorporation of which consumes a lot of energy. The body therefore obtains the basic building blocks not only from food, if available
, but also from the recycling of cells.
The ability of cells to recycle decreases significantly with age.
It is easy for the body if nucleotides are available as food supplements and are already individually selected - so they only need to be integrated. They are indispensable for cell division and cell renewal in a healthy metabolism.

Where in the body are nucleotides needed?
Fast-growing cells have a particularly high demand for nucleotides. These include the intestinal mucosa, blood cells, immune cells and, last but not least,
the intestinal bacteria.
The bacteria in the intestinal flora are important for health and well-being: Together they form the microbiome, which exerts an immense influence on the immune system and metabolism. It serves as a constant
sparring partner for the former and makes many nutrients in food available in the first place
. These include substances that are essential for liver function, fat metabolism and the immune system
.
Nucleotides are so important that they are already contained in high
concentrations in our breast milk
. Later on, we are dependent on ingesting them with our food.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) about nucleotides
Nucleotides – effects, applications, and the best products from Switzerland. Individually selected nucleotides based on Dr. Peter Köppel's formula.
What effect do nucleotides have on health and performance?
Nucleotides are needed in the body for cell regeneration, the immune system, cell renewal, and energy production. Their effects are based on scientific studies, making them particularly valuable for athletes, health-conscious people, and anyone who wants to increase their vitality.
Where can I buy high-quality nucleotides?
The best nucleotides are available in Switzerland as individually selected nucleotides, e.g. from Vegana Natura. When purchasing, look for individually selected nucleotides and Swiss-made products. These are also vegan, low in allergens, and meet the highest quality standards—for maximum safety and effectiveness.
What distinguishes the best nucleotide supplements?
The best nucleotides are individually selected, highly pure, optimally bioavailable, and manufactured under strict quality controls. Vegana Natura relies on scientifically based formulations, Swiss-
-quality, and absolute transparency regarding ingredients and origin.
For whom is taking nucleotides beneficial?
Nucleotide supplements are particularly suitable for athletes, people undergoing periods of increased stress or recovery, vegetarians and vegans, as well as anyone who wants to support their immune system and cell health.
Is there scientific evidence for the effectiveness of nucleotides?
Yes, numerous studies confirm the positive effect of nucleotides
on immune function, regeneration, and intestinal health. Renowned biochemist and immunologist Dr. Peter Köppel has published numerous articles on this topic.
