Nucleotides - the building blocks of life
The most important facts at a glance
Nucleotides: effect, function & structure
Discover the diverse effects and precise functions of nucleotides. Immerse yourself in the world of these essential building blocks, which not only store genetic information and regulate gene expression, but also enable central processes for cell health and regeneration. Scientific findings show that nucleotides can make a significant contribution to supporting the immune system, intestinal function, and general well-being—always taking into account the latest studies and without making exaggerated health claims. and can contribute to increasing well-being.
Learn moreNucleotides and the gut: influence on gut health
The intestine – a key organ for our health. Scientific studies show that nucleotides specifically support intestinal function and can make an important contribution to a balanced immune defense. Through their role in cell regeneration and metabolism, nucleotides promote a stable intestinal barrier and a healthy microbiome – for greater well-being and a strong immune system.
Learn moreNucleotides: All experiences at a glance
Find out at a glance what experiences users have had with nucleotides. Many users report that high-quality nucleotides specifically support the immune system, promote tissue regeneration, and can contribute to maintaining a healthy immune balance. Scientific findings also suggest that nucleotides play a role in regulating inflammatory processes.
Learn moreTaking nucleotides: How to do it right
Learn how to take nucleotides correctly to achieve their full effect. Discover the different forms of nucleotides and their specific applications.
Learn moreNucleotides are the basic building blocks of life and play a crucial role in the transfer of genetic information, the storage of genetic information and the regulation of gene expression. In this guide, we take an in-depth look at the various aspects of nucleotides, including their action, function and structure.
We are also investigating the importance of nucleotides for the gut and how they can affect gut health. In addition, we look at the different experiences of people who take nucleotides to improve their health and treat disease. Finally, we go into more detail about taking nucleotides and the effects they have on the body. We hope this guide will deepen your understanding of nucleotides and help you make informed decisions about your health and wellbeing.
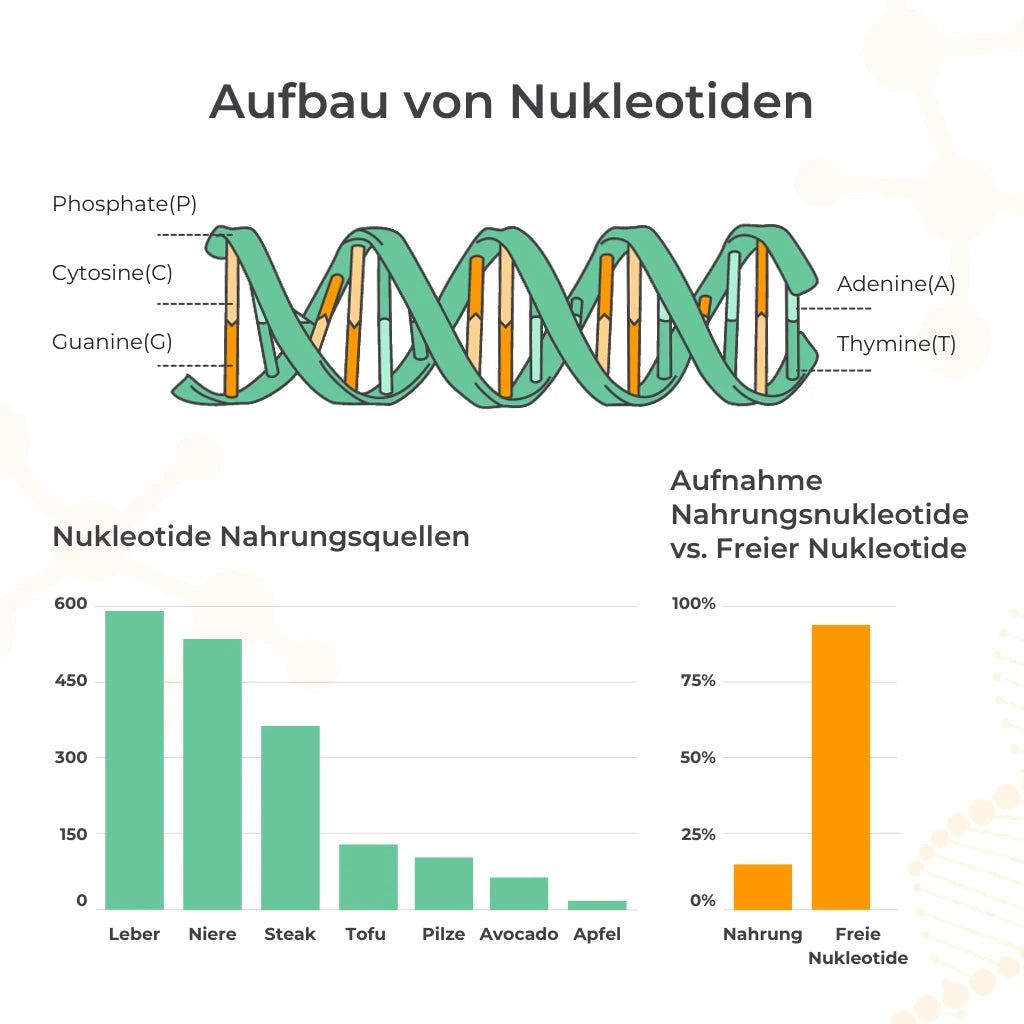
Nucleotides: effect, function & structure
Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA, which contain our genetic information. They consist of three parts: a base, a sugar and a phosphate group. The foundation is that each nucleotide in DNA is unique and carries the information in the DNA molecule. Each base pairing occurs during DNA replication, with each base having a complementary base. The four bases are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T) in DNA or uracil (U) in RNA. The sugar is either ribose (in RNA) or deoxyribose (in DNA). The phosphate group is a molecule that consists of phosphorus and oxygen and is bound to the sugar molecule.
Nucleotides have vital functions in cells. They play an important role in the transmission of signals and in energy production. For example, ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a nucleotide that serves as a universal energy carrier in cells. It is converted into energy in many metabolic processes and provides the necessary drive for all cellular processes.
Nucleotides are not only essential for our cell division and energy metabolism in our mitochondria, but also for the formation of fats and carbohydrates. Without nucleotides, our body would not be able to carry out important processes that are necessary for survival. These include cell division, which is responsible for the growth and repair of tissues and organs in the body.
Nucleotides also ensure that proteins are better absorbed and transported, the immune system is strengthened by promoting the production of antibodies, and cell renewal is supported, which is important for healthy tissue.
Nucleotides are also essential for DNA replication and protein biosynthesis. During DNA replication, the two strands of the DNA double helix are separated, with the nucleotides serving as a template for the construction of new DNA strands. During protein biosynthesis, the information in the DNA is transcribed into RNA, which then serves as a template for the production of proteins.
Nucleotides also play an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases and cancer. Genetic analysis of nucleotides can identify specific mutations and abnormalities that may indicate disease. Based on this information, personalized therapies can be developed that are tailored to the individual genetic background.
Here you can find out more about the the effect, function and structure of a DNA nucleotide. here.
Here are some vegan food supplements that contain nucleotides
Nucleotides and the gut
Nucleotides are abundant in the intestine, as this part of the digestive tract is responsible for the breakdown of food and the absorption of nutrients. Some nucleotides, such as adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and guanosine monophosphate (GMP), are released by the breakdown of nucleic acids from food.
These nucleotides have various functions in the intestine. On the one hand, they serve as an energy source for the intestinal cells and support their normal function. They can also promote intestinal health by stimulating the growth and activity of beneficial intestinal bacteria. These bacteria are important for digestion, the absorption of nutrients and the defense against pathogenic germs. This can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight, for example.
The intake of nucleotides can also have a positive effect on the composition of the intestinal flora. Nucleotides can also strengthen the intestinal barrier and reduce inflammation in the intestine. Thanks to these diverse effects, nucleotides can contribute to improving intestinal health. They can be taken in the form of food supplements to cover the intestine's nucleotide requirements and support intestinal function.
For more information, you can read our article on the importance of nucleotides in the gut in the gut.

Vegan supplements for weight control that contain nucleotides
Experiences of our customers
"As a vegan, endurance athlete and iron-man triathlete, I have a special need for nutrients for my body and am constantly on the lookout for healthy and energy-boosting ingredients that are healthy for my body and, very importantly for me personally, are also natural!"
Taking nucleotides
Nucleotides can be taken in a variety of ways, including through food and supplements. Nucleotides are found in many foods, especially protein-rich foods such as meat, fish, eggs and legumes. You can find food supplements containing nucleotides on our website. We worked together with a renowned Swiss researcher who has been researching nucleotides for 30 years and developed high-quality products that contain nucleotides and are vegan. These include capsules, tablets and powders. The recommended dosage of nucleotides depends on various factors, including a person's age, gender and state of health.
Would you like more information about taking nucleotides? Then take a look at our article "Taking nucleotides" and find out what other foods they can be found in.
More matching blog articles on the topic of nucleotides
Frequently asked questions about nucleotides
Nucleotides play a crucial role in the cell. They serve as building blocks of DNA and RNA, which store genetic information. Nucleotides are also responsible for the transfer of chemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and are involved in various signal transduction processes.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are both nucleic acids, but they have some differences. DNA contains the sugar base deoxyribose and the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine. RNA contains the sugar base ribose and the bases adenine, uracil, cytosine and guanine.
Nucleotides are found in many foods, especially in protein-rich foods such as meat, fish, eggs and dairy products. Pulses, nuts and seeds also contain nucleotides. Furthermore, nucleotides are contained in yeast extract and brewer's yeast, which are often used as food supplements. Some manufacturers also offer nucleotide preparations in the form of capsules or powder, which can be taken as a dietary supplement.
The best nucleotides are individually selected nucleotides due to their higher bioavailability. There are four types of nucleotides that occur in DNA and RNA. Nucleotides consist of sugar, phosphate groups, and four bases. The four bases in DNA are adenine (abbreviation: A), guanine (abbreviation: G), cytosine (abbreviation: C), and thymine (abbreviation: T). In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil (abbreviation: U).
A human being has around 3 billion nucleotides in every single cell. The body of an adult human consists of around 100 trillion cells. These figures show how important the small molecules "nucleotides" are.
Yes, it makes sense to supplement with good nucleotides if you have specific needs. Make sure you choose high-quality products with individually selected nucleotides, such as Vegana Natura. Nucleotides are produced by the body itself, and supplementation is not absolutely necessary if you have a healthy and balanced diet.
Any further questions?
If you have any further questions or need more information, please do not hesitate to contact us. We will be happy to help you with any questions you may have about nucleotides.
Our conclusion
Nucleotides form the framework of DNA and RNA, which contain our genetic information. The structure of nucleotides is made up of three components: a base, a sugar and a phosphate group. The four different bases are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T) in DNA or uracil (U) in RNA. The sugar can be either ribose (in RNA) or deoxyribose (in DNA). The phosphate group is a molecule that consists of phosphorus and oxygen and is bound to the sugar molecule.
Nucleotides are important for the health and well-being of the body. For example, they are essential for cell division, energy metabolism and the breakdown of fats and carbohydrates. They also help with the absorption and transport of proteins, strengthen the immune system, support cell renewal and are crucial for DNA replication and protein synthesis.
Interestingly, they are abundant in the gut. Here they serve as an energy source for intestinal cells and can promote intestinal health by stimulating the growth and activity of beneficial intestinal bacteria. They can also strengthen the intestinal barrier and reduce inflammation in the gut.
Taking nucleotides through food or supplements can therefore have a positive effect on the immune system, energy levels, digestion and muscle regeneration. They are suitable for athletes, vegans and vegetarians, people of an older age and people who simply value their health. However, it is important to consult a doctor or nutritionist before taking nucleotide supplements, as excessive intake can lead to side effects.









